Best Anti-Aging Herbal Supplements Review

Anti-aging herbal supplements fascinate us in our quest to maintain youthful vitality and appearance. These supplements cannot reverse or stop aging completely, yet they show promising benefits that may help delay age-related conditions.
Scientific evidence shows anti-aging supplements work through their antioxidant effects to reduce cell damage and inflammation. Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) levels naturally decline with age, but research proves supplementation can improve skin health and reduce wrinkles. A 12-week study showed reduced wrinkles and improved skin smoothness in participants taking oral CoQ10 supplements.
Fisetin, found in fruits and vegetables, targets senescent cells and could improve health span, though more human studies are needed. The active compound in turmeric, curcumin, has powerful cellular protective properties that curb damage at the cellular level.
Many people are surprised by these supplements’ effectiveness for specific aging concerns. Research has shown collagen supplements substantially improve skin’s hydration and elasticity, which results in smoother skin with fewer lines. Green tea’s EGCG compounds help prevent amyloid buildup linked to Alzheimer’s disease and suppress brain aging while reducing stress.
Our analysis will get into the most effective anti-aging herbal supplements, their scientific backing, proper dosages, and specific benefits for different aging aspects.
📺 **Watch Now: Best Anti-Aging Herbal Supplements Review**
Fisetin
Fisetin stands out as one of the most promising natural compounds for anti-aging because of its powerful biological effects. Scientists are really interested in this flavonoid that exists in many fruits and vegetables. It can target basic aging processes right at the cellular level.
Fisetin benefits for aging
Fisetin belongs to the polyphenol family of compounds. It’s a flavonoid that gives fruits and vegetables their bright colors. This plant compound works in several ways to curb aging. It acts as a senolytic agent that removes senescent or “zombie” cells which build up as we age [1].
These senescent cells are damaged and won’t die naturally. They keep releasing harmful substances that hurt healthy cells around them. These problematic cells make tissues work poorly and speed up aging. Fisetin clears these cells away to restore tissue balance and help us live longer [2].
Fisetin does more than just remove senescent cells – it’s also a powerful antioxidant. It neutralizes harmful free radicals and helps our body make more glutathione, our most important antioxidant [1]. This two-way approach prevents oxidative damage to cells, proteins, and DNA that leads to aging.
Fisetin works like calorie restriction, which helps people live longer and stay healthier. It triggers similar biological pathways:
- It reduces mTOR activity (a protein linked to aging)
- It makes sirtuins work better (proteins that keep cells healthy)
- It increases AMPK activity (an enzyme that manages metabolism)
- It promotes autophagy (cellular “housekeeping”) [1]
Scientific evidence supporting Fisetin
Research shows strong anti-aging effects from fisetin, especially in animal studies. Mice that got fisetin later in life lived 10% longer [2]. These mice had fewer age-related problems and their tissues worked better.
Lab tests of various flavonoids showed fisetin worked best at removing senescent cells among ten different compounds [1]. Older mice that received fisetin had fewer senescence markers in their kidneys, liver, and fat tissue [1].
A 2018 study showed how fisetin treatment helped both progeroid mice (with fast aging) and naturally aged mice. It cleared senescent cells from fat tissue and other organs [1].
Human studies are just starting to emerge. A small trial gave people over 50 years old 500mg of fisetin daily for one week each month over six months. The results varied – four people aged more slowly, five aged faster, and one stayed the same [1]. We need bigger human trials to know more.
Notwithstanding that, fisetin works well in human cell studies. It removed many senescent cells from human umbilical vein endothelial cells [1]. It worked better than other plant-based senolytics like quercetin at destroying senescent cells in human cell cultures [3].
Fisetin dosage and safety
Scientists still need to find the best fisetin dose because human research is limited. Most supplements contain 100-500mg per capsule [1]. Current clinical trials test about 20mg/kg of body weight [1], which means higher doses for adults.
Toxicity studies show fisetin is quite safe. Mice can handle very high oral doses – up to 1700mg/kg [1]. But intravenous doses should not exceed 200mg/kg [1].
Many experts suggest taking fisetin for a few days each month instead of daily. This helps clear senescent cells without affecting normal processes like wound healing [3].
Fisetin breaks down quickly after you take it. New breakthroughs have fixed this by mixing it with fenugreek galactomannans, which makes it absorb 25 times better [3]. Taking it with fatty foods helps absorption since it dissolves in fat [1].
Watch out for interactions with:
- Blood thinners (might increase bleeding risk)
- Cancer treatments (might affect how well they work) [1]
Fisetin for skin and brain health
Fisetin helps skin health in several ways. It protects skin from UV damage and toxins [1]. It makes skin look better by reducing enzymes that break down collagen and elastin [1].
Animals studies show fisetin reduced wrinkles and visible aging signs [1]. It might help treat skin inflammation like eczema too [1].
The brain benefits really stand out. Research shows fisetin makes memory and thinking better [1]. It keeps neurons safe from oxidative stress and helps the brain make new connections.
In Alzheimer’s studies, fisetin stopped harmful proteins like beta-amyloid and hyperphosphorylated tau from building up [1]. It helped brain cells clear out existing toxic proteins.
A recent study with aged sheep showed fisetin reduced senescent brain cells, including neurons, microglia, and astrocytes [2]. Blood tests showed lower S100B levels, which means less brain damage [2].
Mice with Huntington’s disease lived 30% longer when fed fisetin [1]. Their movement problems started later too.
To learn more about fisetin, check these trusted sources:
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Mayo Clinic Kogod Center on Aging (www.mayo.edu/research/centers-programs/kogod-center-aging)
- National Institute on Aging (www.nia.nih.gov)
Curcumin
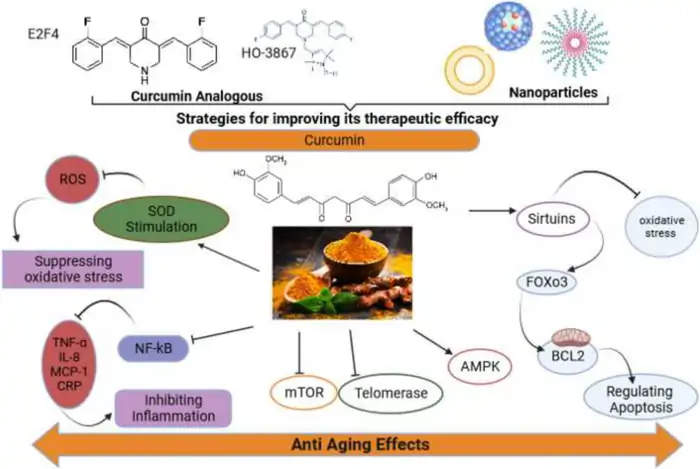
Image Source: link.springer.com
The golden-yellow spice turmeric has been a staple in Asian medicine cabinets and kitchen shelves for centuries. Curcumin, a powerful polyphenolic compound, makes up just 2-5% of turmeric but delivers most of its health benefits [1]. Modern science now proves right what traditional healers knew all along – curcumin has remarkable anti-aging properties.
Curcumin benefits for aging
Natural anti-aging supplements often target single pathways. Curcumin stands out because it works on multiple aging pathways at once. This versatile compound works through several key mechanisms:
- Removes senescent cells: Curcumin works as a senolytic agent that eliminates dysfunctional “zombie” cells. These cells build up with age and release harmful inflammatory compounds [1]. Mouse studies showed it brought senescent cells back to normal levels [1].
- Lengthens telomeres: The compound boosts telomerase expression and activity. This enzyme adds new DNA to telomere ends and helps maintain cellular function [1].
- Activates longevity pathways: Curcumin affects key aging regulators like AMPK (supporting metabolism), sirtuins (protecting cells), and autophagy (cellular housekeeping) [1].
- Reduces glycation: The compound protects proteins from sugar molecule damage that speeds up aging and leads to conditions like cataracts [1].
- Protects mitochondria: Curcumin boosts mitochondrial health and improves cellular energy production [1].
Oxidative stress drives aging faster than most factors. Curcumin fights it by neutralizing free radicals and strengthening natural antioxidant defenses. Studies show it boosts superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity while lowering harmful malondialdehyde (MDA) and lipofuscin levels [2].
Scientific evidence supporting Curcumin
Research backing curcumin’s anti-aging effects runs deep. Fruit flies lived 26% longer with curcumin [1]. Scientists have showed this lifespan extension consistently across nematodes, yeast, and mice [2].
Curcumin extends life by changing major longevity pathways. Like rapamycin, a prominent anti-aging compound, it reduces mTOR activity – a protein linked to faster aging [1]. The compound also activates AMPK, which helps control metabolism and extends lifespan in various organisms [3].
More studies show curcumin blocks NF-κB signaling that controls inflammation and aging [3]. It also lifts sirtuin activity – especially SIRT1 – which guards against DNA damage and mutations [3]. These proteins usually become less active with age, and boosting them has extended life in animal studies.
Lab studies tell only part of the story. Human trials paint an encouraging picture too. People taking curcumin showed better cognition and memory than those on placebo [1]. Another study found 80 mg/day of curcumin nanomicelles by a lot improved plasma C-reactive protein levels, which indicate inflammation [3].
Curcumin dosage and safety
Poor absorption makes finding the right curcumin dose tricky. Most research uses 500-2,000 mg daily [1], usually as extract rather than whole turmeric. Turmeric spice contains about 3% curcumin, while extracts pack 95% [1].
The World Health Organization (WHO) says you can safely take 0-3 mg per kilogram of body weight each day [1]. Studies show curcumin remains safe even at high doses – up to 12 grams daily for 3 months caused no toxic effects [1].
The safety profile looks great, but some people should be careful with curcumin supplements:
- People with gallbladder disease
- Those on blood-thinning medications
- Individuals with diabetes (may lower blood sugar)
- Those with iron deficiency
The biggest problem with curcumin is poor absorption. The body poorly absorbs standard curcumin, breaks it down fast, and removes it quickly [4]. Scientists have created better formulations that boost absorption:
- Piperine combination: Black pepper extract (piperine) made curcumin absorption 2,000% better in human studies [4].
- Phytosome complexes: Mixing curcumin with phospholipids (like Meriva) showed 29 times better absorption [4].
- Fenugreek combination: Adding galactomannans from fenugreek increased blood levels 45 times compared to plain curcumin [5].
Curcumin for inflammation and longevity
Low-grade chronic inflammation – “inflammaging” – drives many age-related diseases [3]. Age weakens regulatory systems, which leads to higher inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP), IL-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) [3].
Curcumin fights inflammation head-on. It blocks the NF-κB pathway and reduces inflammatory compounds that speed up cellular aging [3]. Studies show even small doses lower pro-inflammatory cytokines in normal cells [3].
The compound helps with specific age-related conditions too. Clinical trials prove it helps arthritis patients. Studies show less pain on both Visual Analog Scale (VAS) and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) [6]. Patients also move better and feel less stiff [6].
Brain health gets multiple benefits from curcumin. The compound reduces brain inflammation, improves neuroplasticity, and boosts important growth factors like BDNF, NGF, and GDNF [3]. These changes lead to better thinking and protect against age-related brain problems.
Learn more about curcumin’s benefits at these trusted sources:
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- World Health Organization (www.who.int)
- National Institute on Aging (www.nia.nih.gov)
EGCG (Green Tea Extract)

Image Source: Amazon.com
The simple tea leaf from the Camellia sinensis plant contains one of nature’s most powerful anti-aging compounds—epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). This compound stands out as the most abundant and active polyphenol in green tea. EGCG leads the pack among natural anti-aging supplements and works in multiple ways to curb aging at the cellular level.
EGCG benefits for aging
EGCG slows aging and supports longevity through several mechanisms:
Powerful antioxidant protection: EGCG protects cells from oxidative damage 100 times better than vitamin C and 25 times better than vitamin E [7]. This exceptional ability helps neutralize free radicals that speed up cellular aging.
Senescent cell reduction: EGCG helps manage senescent or “zombie” cells that build up as we age. Studies in mice showed EGCG substantially reduced senescence markers and helped preserve tissue function [2].
Activation of longevity pathways: EGCG gets more AMPK, SIRT1, and FOXO proteins working [8]. These proteins regulate cellular energy, stress resistance, and repair mechanisms needed for healthy aging.
Mitochondrial support: EGCG boosts mitochondrial production to restore function [8]. This tackles one of the basic parts of cellular aging—declining energy production.
The sort of thing I love about EGCG is its hormetic effect. It causes a small increase in reactive oxygen species at first. This activates the body’s natural antioxidant defenses and leads to lower oxidative stress over time [8]. Scientists call this mitohormesis, which might explain why EGCG works better when people start taking it earlier in life.
Scientific evidence supporting EGCG
Lab work, animal studies, and human research back up EGCG’s anti-aging effects. One fascinating experiment found that 2.5 μM of EGCG helped C. elegans (a common research organism) live 6.9% longer. These organisms also showed better stress resistance and physical performance [2].
Research revealed something even more interesting. EGCG supplements work differently based on when people start taking them. Starting in early-to-mid adulthood brought better longevity benefits than beginning later in life [8]. This suggests timing matters a lot for anti-aging treatments.
Studies from Japan provide more supporting evidence. Older people who drank green tea regularly over five years were 68% less likely to develop dementia and mild cognitive problems compared to those who didn’t drink tea [4]. People who had two or more cups daily also showed fewer signs of cognitive decline [4].
Clinical trials on skin aging brought measurable improvements. One study showed that green tea extract substantially improved elastic tissue content in skin biopsies [6]. Other research confirmed that green tea can slow down collagen aging through its antioxidant properties [9].
EGCG dosage and safety
The right EGCG dose balances effectiveness with safety. Most supplements contain 250-500 mg of EGCG daily, which equals about 3-5 cups of green tea (1.2 liters) [1]. Clinical studies used amounts from 90-800 mg daily [10].
Traditional green tea (brewed normally) appears safe for most people [10]. But some caution helps. The European Food Safety Authority notes that supplement doses above 800 mg EGCG daily might increase liver problems [10]. A large study with over 500 people taking 843 mg EGCG daily for a year found that 5.1% had moderate or worse liver issues [10].
Key safety tips include:
- Take EGCG supplements with food to protect your liver [1]
- Stay within recommended doses, especially with concentrated extracts
- Pregnant women should talk to their doctors before using EGCG supplements
- People with low iron should be careful since EGCG might reduce iron absorption
EGCG for skin and cognitive health
EGCG helps skin health in several ways. It guards against UV radiation damage by lowering oxidative stress and inflammation in skin cells [3]. Your skin’s elasticity improves because EGCG blocks enzymes that break down collagen and elastin [3]. This preserves your skin’s structural foundation.
Lab studies showed EGCG improved overall skin conditions in aging models. It enhanced the whole skin structure and reduced oxidative stress markers [3]. These improvements came from EGCG’s interaction with epidermal growth factor receptors, which help skin cells regenerate and repair [11].
EGCG crosses the blood-brain barrier to protect brain cells directly [12]. It removes harmful free radicals in neural tissue and reduces inflammation-causing proteins like TNF-α and IL-1β, which increase during brain disorders [12].
EGCG also protects against age-related cognitive decline by:
- Blocking beta-amyloid production linked to Alzheimer’s disease [4]
- Boosting new nerve cell growth and brain adaptability [12]
- Protecting against social withdrawal and spatial reasoning problems [4]
- Making working memory tasks faster [4]
To learn more about EGCG benefits, check out these trusted sources:
- National Institutes of Health (www.nih.gov)
- European Food Safety Authority (www.efsa.europa.eu)
- Mayo Clinic (www.mayoclinic.org)
Ashwagandha
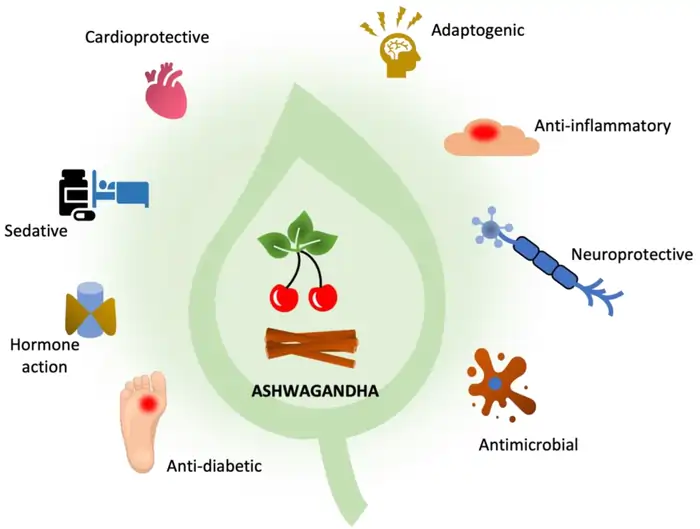
Image Source: MDPI
Ayurvedic medicine has long valued Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) as a Rasayana herb. It’s one of the most effective natural anti-aging supplements in traditional healing. People know this adaptogenic herb as “Indian Winter cherry” or “Indian Ginseng.” They’ve used it for over 3,000 years to boost vitality and curb age-related decline.
Ashwagandha benefits for aging
Ashwagandha works in several ways to slow down aging:
- Enhanced longevity pathways: Research shows Ashwagandha can extend lifespan in C. elegans (a common organism used in longevity research) [13]. This suggests it activates basic aging mechanisms.
- Telomerase promotion: The root extract boosts telomerase activity by about 45% in human cell lines. This helps protect chromosomal integrity [14].
- Senescent cell reduction: Just like other effective anti-aging supplements, Ashwagandha helps control cellular senescence that leads to tissue aging.
- Potent antioxidant activity: It fights free radicals and lowers oxidative stress that speeds up aging.
Ashwagandha also protects brain function and may prevent age-related cognitive decline. It helps fight Alzheimer’s disease by reducing β-amyloid buildup and stopping τ protein accumulation [15].
Scientific evidence supporting Ashwagandha
Lab and human studies back up Ashwagandha’s anti-aging benefits. Mice that received Ashwagandha root extract lived longer than those that didn’t [13].
Human trials look promising too. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that people taking Ashwagandha root extract had lower stress levels and less serum cortisol—a stress hormone that speeds up aging [5].
Research keeps showing that Ashwagandha lowers cortisol levels by a lot. People who took 225–400 mg daily for a month saw big drops in cortisol [16]. Another study found that 600 mg daily for eight weeks helped people sleep better and feel less anxious [16].
Ashwagandha dosage and safety
Research points to effective doses between 250–600 mg of root extract daily. Higher doses work better for sleep [5]. Most supplements on the market offer 300–500 mg per dose [16].
You can take Ashwagandha supplements with or without food. They come as capsules, tablets, and powder. Extracts with standardized withanolides (the active compounds) work more reliably [16].
Ashwagandha is safe for most people to take up to 3 months [3]. However, some people should be careful:
- Pregnant women (risk of miscarriage)
- Breastfeeding mothers
- People with autoimmune conditions
- Those with thyroid issues (may raise thyroid hormone levels)
- Anyone scheduled for surgery
- People taking diabetes or blood pressure medicine [3]
Ashwagandha for stress and vitality
Ashwagandha’s biggest anti-aging benefit might be its power to fight stress—which makes us age faster. Studies show it lowers stress scores and physical stress markers [5].
The herb also helps you sleep better, which is vital for healthy aging. A 2021 review found that taking at least 600 mg daily for eight weeks helped people with stress or insomnia sleep better and feel less anxious [16].
Physical benefits are impressive too. Studies show that combining Ashwagandha with resistance training for 12 weeks can build muscle mass and strength [16]. Men also see healthy testosterone levels and better reproductive function [16], which naturally decline with age.
You can learn more about Ashwagandha’s anti-aging benefits from these trusted sources:
- National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (www.nccih.nih.gov)
- U.S. National Library of Medicine (www.pubmed.gov)
- Office of Dietary Supplements (ods.od.nih.gov)
Resveratrol
Red wine, grapes, and berries contain resveratrol, which has caught the attention of anti-aging researchers. This powerful polyphenol compound is an antioxidant that protects the body against damage and reduces the risk of age-related conditions [17].
Resveratrol benefits for aging
Resveratrol’s anti-aging effects come from its ability to activate the SIRT1 gene that protects against obesity effects and age-related diseases [17]. Here’s how it works:
- Acts like calorie restriction to activate longevity pathways [2]
- Helps cellular “housekeeping” (autophagy) in aging tissues [8]
- Fights oxidative stress with antioxidant properties [18]
- Reduces chronic inflammation tied to aging [10]
Resveratrol provides neuroprotective benefits that might slow cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s patients [8]. The compound protects against age-related DNA and RNA oxidative damage while it boosts cognitive performance [8].
Scientific evidence supporting Resveratrol
Lab research shows impressive results. Resveratrol helps extend lifespan in a variety of organisms like yeast, worms, and flies [2]. Studies with older mice on high-calorie diets showed better insulin sensitivity, fewer insulin-like growth factors, more mitochondria, and improved motor functions [8].
Tests on non-human primates showed that resveratrol reduced body mass without changing their natural movement [8]. It also prevented mitochondrial loss and helped with muscle cell maintenance [8].
Over the last 20 years, scientists have conducted nearly 200 clinical studies to review resveratrol’s safety and effects in humans [10]. These studies showed better glucose metabolism, improved cardiovascular markers, and less oxidative stress and inflammation [8].
Resveratrol dosage and safety
Most supplements have 250-500 mg of resveratrol, though research often uses higher doses [17]. You’d need about 2 grams (2,000 mg) daily to match doses from promising studies [17].
High doses haven’t shown serious side effects in safety studies [17]. However, you should be careful if you have:
- Bleeding disorders [7]
- Take blood thinners, blood pressure medications, or NSAIDs [17]
- Diabetes (it may affect blood sugar) [7]
Resveratrol for heart and skin health
Resveratrol helps heart health by reducing inflammation, lowering LDL cholesterol, and preventing blood clots that can cause heart attacks [17]. It boosts cardiovascular health by increasing nitric oxide production and fighting oxidative stress [18].
Your skin benefits as resveratrol protects against UVB radiation damage—the main cause of skin aging [19]. On top of that, it helps produce more collagen by activating estrogen receptors and reduces wrinkles [19]. Research confirms that resveratrol speeds up skin healing and regeneration by activating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) [19].
To learn more about resveratrol, check out these trusted sources:
- National Institutes of Health (www.nih.gov)
- Mayo Clinic (www.mayoclinic.org)
- World Health Organization (www.who.int)
Comparison Table
Anti-Aging Herbal Supplements Comparison Table
| Supplement | Key Benefits | Primary Mechanisms | Scientific Evidence | Recommended Dosage | Safety Considerations | Specific Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fisetin | – Targets aging processes at cellular level – Promotes longevity – Reduces cellular damage | – Acts as senolytic agent – Boosts glutathione production – Mimics calorie restriction benefits | – 10% increase in median lifespan (mice) – The most potent senolytic among all but one of these candidates tested | 100-500mg per capsule Intermittent dosing recommended | – High safety profile – May interact with anticoagulants – Best absorbed with fatty foods | – Protects skin from UV damage – Boosts memory formation – Improves cognitive function |
| Curcumin | – Multi-pathway aging benefits – Reduces inflammation – Protects DNA | – Removes senescent cells – Lengthens telomeres – Activates longevity pathways | – 26% lifespan extension in fruit flies – Improved cognition in human trials | 500-2,000mg daily | – Safe up to 12g daily – Caution with gallbladder disease – May interact with blood thinners | – Reduces arthritis symptoms – Improves brain function – Decreases inflammation |
| EGCG | – Powerful antioxidant protection – Cellular aging prevention – Mitochondrial support | – 100x more effective than Vitamin C – Reduces senescent cells – Activates longevity pathways | – 6.9% lifespan extension in C. elegans – 68% lower dementia risk in humans | 250-500mg daily | – Safe below 800mg daily – Take with food – May affect iron absorption | – Protects against UV damage – Boosts skin elasticity – Improves cognitive function |
| Ashwagandha | – Boosts vitality – Reduces stress – Promotes longevity | – Boosts telomerase activity – Reduces oxidative stress – Manages cellular senescence | – Most important lifespan extension in mice – Reduces cortisol levels in humans | 250-600mg daily | – Safe for up to 3 months – Avoid during pregnancy – May affect thyroid function | – Improves sleep quality – Increases muscle mass – Reduces anxiety |
| Resveratrol | – Activates longevity genes – Reduces oxidative stress – Promotes cellular health | – Activates SIRT1 gene – Promotes autophagy – Reduces inflammation | – Extends lifespan in multiple species – Improves metabolism in clinical studies | 250-500mg daily (up to 2,000mg in studies) | – Generally safe – May interact with blood thinners – Can affect blood sugar | – Improves heart health – Protects skin from UV damage – Boosts collagen synthesis |
Recommended Resources:
- National Institutes of Health (www.nih.gov)
- Mayo Clinic (www.mayoclinic.org)
- World Health Organization (www.who.int)
Conclusion
These five anti-aging supplements show an interesting pattern. Fisetin, Curcumin, EGCG, Ashwagandha, and Resveratrol target basic aging processes through multiple pathways. Each supplement brings unique benefits to the table. They work together to curb oxidative stress, reduce inflammation, and target senescent cells.
Scientific evidence proves these supplements can positively affect longevity pathways. Fisetin stands out as the most powerful senolytic among all studied supplements and shows great potential to extend lifespan. Curcumin’s ability to lengthen telomeres and reduce inflammation makes it impressive too. EGCG’s exceptional antioxidant properties protect cells from damage and support brain health. Ashwagandha excels at reducing stress and boosting vitality. Resveratrol activates the significant SIRT1 longevity gene.
These supplements can’t replace an all-encompassing approach to healthy aging. You need balance when you think about taking these supplements. The right dosage is crucial – taking more than recommended rarely helps and might increase side effects. Starting these supplements early in life tends to work better than beginning later.
Supplements like Curcumin and Fisetin face absorption challenges. This is a big deal as it means that improved formulations become necessary to get optimal results. Quality matters in supplement selection. Standardized extracts with proven absorption boosters usually give more reliable benefits.
You should always ask your healthcare provider before starting new supplements, especially if you have health conditions or take medications. These powerful compounds interact with basic biological processes and could affect how well your medications work.
The National Institutes of Health (www.nih.gov), Mayo Clinic (www.mayoclinic.org), and the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (www.nccih.nih.gov) are great resources to learn more.
The science behind herbal anti-aging supplements grows faster every day. New research will reveal more about how these amazing compounds can help us age healthily and live longer.
FAQs
What are some of the most effective anti-aging herbal supplements?
Some of the most effective anti-aging herbal supplements include Fisetin, Curcumin, EGCG (from green tea), Ashwagandha, and Resveratrol. These compounds work through multiple pathways to combat cellular aging, reduce oxidative stress, and promote longevity.
How does Curcumin contribute to anti-aging effects?
Curcumin, found in turmeric, offers anti-aging benefits by removing senescent cells, lengthening telomeres, and activating longevity pathways. It also reduces inflammation and protects against oxidative stress, which are key factors in the aging process.
What are the potential benefits of EGCG for cognitive health?
EGCG, the main active compound in green tea, may help protect against age-related cognitive decline. It has been shown to inhibit beta-amyloid production associated with Alzheimer’s disease, enhance neuroplasticity, and improve working memory performance.
How does Ashwagandha support healthy aging?
Ashwagandha promotes healthy aging by reducing stress levels, improving sleep quality, and enhancing overall vitality. It also shows potential in activating telomerase, managing cellular senescence, and providing neuroprotective effects that may help prevent age-related cognitive decline.
Are there any safety concerns when taking anti-aging herbal supplements?
While these supplements are generally considered safe, there are some precautions to consider. For example, high doses of EGCG may affect liver function, Curcumin can interact with blood thinners, and Ashwagandha may affect thyroid hormone levels. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking medications.
References
[1] – https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-benefits-of-green-tea-extract
[2] – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925443915000216
[3] – https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/ashwagandha
[4] – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7570631/
[5] – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6979308/
[6] – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16029678/
[7] – https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-307/resveratrol
[8] – https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/genetics/articles/10.3389/fgene.2024.1393181/full
[9] – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3561737/
[10] – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10815776/
[11] – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0047637416302603
[12] – https://www.explorationpub.com/Journals/en/Article/100673
[13] – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4117092/
[14] – https://www.nutraingredients.com/Article/2016/11/23/Ashwagandha-root-extracts-shows-anti-aging-effect-Cell-study/
[15] – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10147008/
[16] – https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/ashwagandha-dosage
[17] – https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/resveratrol-supplements
[18] – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8289612/
[19] – https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9326919/






